Page Speed
Page Speed
Page speed, or the load time of a web page, refers to the amount of time it takes for a web page to fully load and display for the user. It is measured from the moment a visitor requests a page until all content—images, text, videos, and scripts—has fully loaded. Page speed is typically expressed in seconds and is a crucial factor for both user experience and search engine optimization (SEO).
A fast page speed means that a web page loads quickly, resulting in a smooth and pleasant user experience. On the other hand, slow page speed can frustrate users and deter them from further navigating your website.
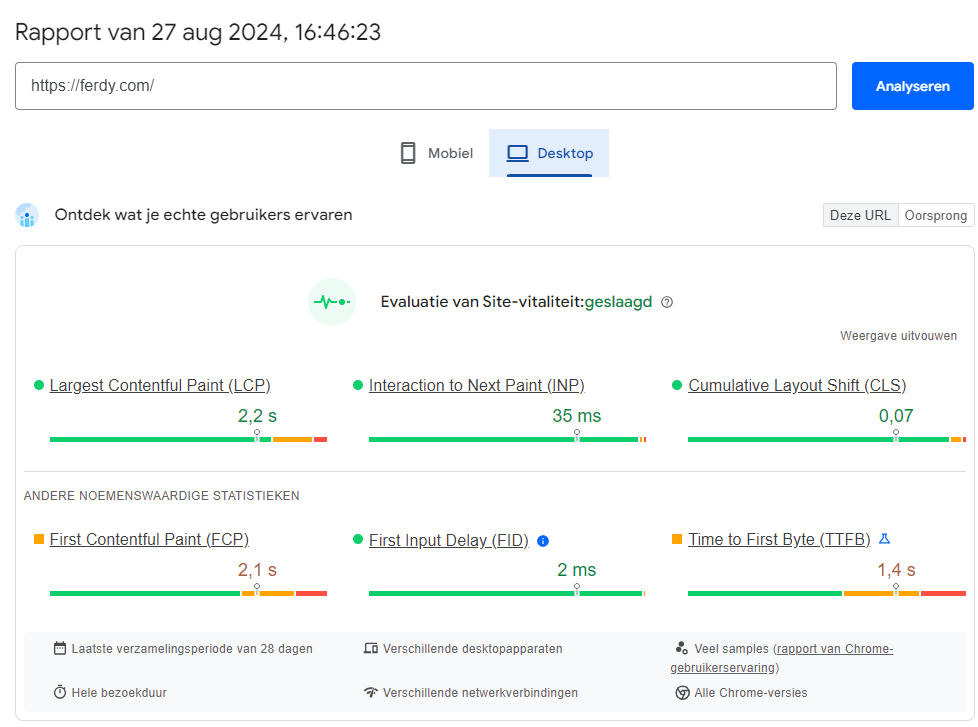
Pagespeed Insights – Ferdy.com
Why is Page Speed Important?
Page speed has multiple important implications for both user experience and SEO.
1. User Experience
The speed at which your website loads has a direct impact on the user experience. Visitors expect web pages to load quickly, and if a page is slow, they may become frustrated and leave the site. Studies have shown that even a one-second delay in load time can result in a significant drop in customer satisfaction and conversions.
2. Conversion Rates
A slow website can negatively impact conversion rates. Visitors are less likely to make purchases, fill out forms, or take other desired actions if your page load time is too long. Faster pages often lead to higher conversions and better user engagement.
3. SEO Rankings
Search engines, especially Google, place great importance on page speed as a ranking factor. Fast pages often rank higher in search results because they offer a better user experience. Google’s algorithms take load times into account when determining search results. A slow website can lead to lower rankings.
4. Mobile Users
With the increasing amount of mobile traffic, page speed has become even more important. Mobile users often have slower internet, making fast load times crucial for ensuring a good experience. Websites optimized for speed will perform better on mobile devices and retain more mobile visitors.
5. Bounce Rate
Slow load times increase the bounce rate, meaning visitors leave the site quickly without exploring further. This not only negatively impacts user experience but can also harm your SEO performance, as search engines may interpret a high bounce rate as a sign of a poor user experience.
How to Measure Page Speed?
There are various tools available to measure and analyze your website’s speed. Some popular tools include:
1. Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights provides detailed reports on the load speed of your pages for both desktop and mobile views. It offers recommendations for improvement and a score indicating how well your page performs.
2. GTmetrix
GTmetrix analyzes your pages for speed and provides insights into load times, file sizes, and other performance aspects. It also offers an overview of areas where improvement is possible.
GTmetrix
3. Pingdom
Pingdom is another popular tool for testing page speed. It provides detailed performance reports and helps you understand how quickly your site loads from different geographic locations.

Pingdom
4. WebPageTest
WebPageTest offers extensive testing options, including the ability to test your pages from different locations and on different devices. It provides in-depth information on your site’s performance.
How to Improve Page Speed?
There are several strategies you can implement to improve your website’s speed.
1. Optimize Images
Images can use a lot of bandwidth and slow down the load time of a page. Optimize images by compressing them without losing quality and using the correct dimensions. Tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim can help with image compression.
2. Minimize HTTP Requests
Each component on a web page (such as images, scripts, and styles) requires an HTTP request. Minimize the number of requests by combining your pages and removing unnecessary elements.
3. Use Browser Caching
Browser caching allows commonly used resources (such as images, CSS, and JavaScript) to be stored in the user’s browser cache so they don’t need to be downloaded again on each visit. This reduces load time for repeat visitors.
4. Implement Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN distributes your website content across multiple servers worldwide, allowing users to retrieve data from a server closer to their location. This can significantly reduce load times, especially for users geographically distant from your main domain.
5. Minimize and Combine CSS and JavaScript
By minimizing and combining your CSS and JavaScript files, you reduce file sizes and the number of HTTP requests. This leads to faster load times and better performance of your website.
6. Remove Unused Plugins and Scripts
Unused or redundant plugins and scripts can slow down your website. Remove plugins you’re not using, and ensure the remaining plugins are properly configured for optimal performance.
WordPress Plugins
7. Optimize Server Response Time
Server response time can affect your website’s speed. Choose a reliable hosting provider and consider upgrading or optimizing your server to improve performance.
8. Use Lazy Loading
Lazy loading ensures that images and other media only load when they come into view during scrolling. This reduces the initial load time of your page and can improve the user experience.
A Better User Experience
Page speed is a
Page Speed
Page speed, or the load time of a web page, refers to the amount of time it takes for a web page to fully load and display for the user. It is measured from the moment a visitor requests a page until all content—images, text, videos, and scripts—has fully loaded. Page speed is typically expressed in seconds and is a crucial factor for both user experience and search engine optimization (SEO).
A fast page speed means that a web page loads quickly, resulting in a smooth and pleasant user experience. On the other hand, slow page speed can frustrate users and deter them from further navigating your website.

Pagespeed Insights – Ferdy.com
Why is Page Speed Important?
Page speed has multiple important implications for both user experience and SEO.
1. User Experience
The speed at which your website loads has a direct impact on the user experience. Visitors expect web pages to load quickly, and if a page is slow, they may become frustrated and leave the site. Studies have shown that even a one-second delay in load time can result in a significant drop in customer satisfaction and conversions.
2. Conversion Rates
A slow website can negatively impact conversion rates. Visitors are less likely to make purchases, fill out forms, or take other desired actions if your page load time is too long. Faster pages often lead to higher conversions and better user engagement.
3. SEO Rankings
Search engines, especially Google, place great importance on page speed as a ranking factor. Fast pages often rank higher in search results because they offer a better user experience. Google’s algorithms take load times into account when determining search results. A slow website can lead to lower rankings.
4. Mobile Users
With the increasing amount of mobile traffic, page speed has become even more important. Mobile users often have slower internet, making fast load times crucial for ensuring a good experience. Websites optimized for speed will perform better on mobile devices and retain more mobile visitors.
5. Bounce Rate
Slow load times increase the bounce rate, meaning visitors leave the site quickly without exploring further. This not only negatively impacts user experience but can also harm your SEO performance, as search engines may interpret a high bounce rate as a sign of a poor user experience.
How to Measure Page Speed?
There are various tools available to measure and analyze your website’s speed. Some popular tools include:
1. Google PageSpeed Insights
Google PageSpeed Insights provides detailed reports on the load speed of your pages for both desktop and mobile views. It offers recommendations for improvement and a score indicating how well your page performs.
2. GTmetrix
GTmetrix analyzes your pages for speed and provides insights into load times, file sizes, and other performance aspects. It also offers an overview of areas where improvement is possible.

GTmetrix
3. Pingdom
Pingdom is another popular tool for testing page speed. It provides detailed performance reports and helps you understand how quickly your site loads from different geographic locations.

Pingdom
4. WebPageTest
WebPageTest offers extensive testing options, including the ability to test your pages from different locations and on different devices. It provides in-depth information on your site’s performance.
How to Improve Page Speed?
There are several strategies you can implement to improve your website’s speed.
1. Optimize Images
Images can use a lot of bandwidth and slow down the load time of a page. Optimize images by compressing them without losing quality and using the correct dimensions. Tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim can help with image compression.
2. Minimize HTTP Requests
Each component on a web page (such as images, scripts, and styles) requires an HTTP request. Minimize the number of requests by combining your pages and removing unnecessary elements.
3. Use Browser Caching
Browser caching allows commonly used resources (such as images, CSS, and JavaScript) to be stored in the user’s browser cache so they don’t need to be downloaded again on each visit. This reduces load time for repeat visitors.
4. Implement Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN distributes your website content across multiple servers worldwide, allowing users to retrieve data from a server closer to their location. This can significantly reduce load times, especially for users geographically distant from your main domain.
5. Minimize and Combine CSS and JavaScript
By minimizing and combining your CSS and JavaScript files, you reduce file sizes and the number of HTTP requests. This leads to faster load times and better performance of your website.
6. Remove Unused Plugins and Scripts
Unused or redundant plugins and scripts can slow down your website. Remove plugins you’re not using, and ensure the remaining plugins are properly configured for optimal performance.

WordPress Plugins
7. Optimize Server Response Time
Server response time can affect your website’s speed. Choose a reliable hosting provider and consider upgrading or optimizing your server to improve performance.
8. Use Lazy Loading
Lazy loading ensures that images and other media only load when they come into view during scrolling. This reduces the initial load time of your page and can improve the user experience.
A Better User Experience
Page speed is a crucial aspect of both user experience and SEO. Fast load times lead to better user experiences, increased conversions, and improved search engine performance. By regularly measuring your page speed and applying the right optimizations, you can ensure your website performs efficiently and effectively.
